目标
会创建类和对象
掌握面向对象的三大特性:封装,继承,多态
掌握抽象类和接口的使用
掌握程序中的异常处理
使用面相对像思维进行编程
机构开发
面向功能划分软件结构
自顶而下
最小的子系统是方法
制约了软件的可维护性可扩展性
面相对像开发
把软件系统看成各种对象的集合
系统结构较稳定
子系统相对于独立
软件可重用性,可维护性和可扩展性强
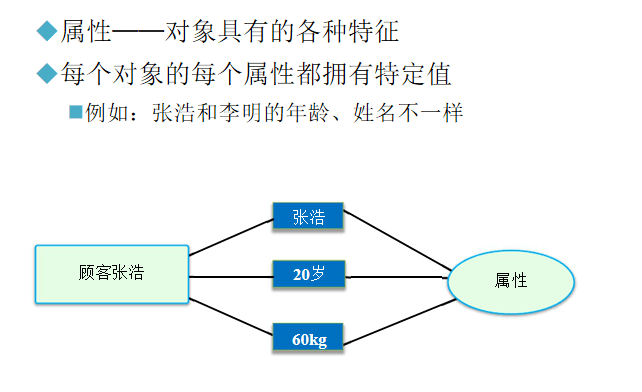
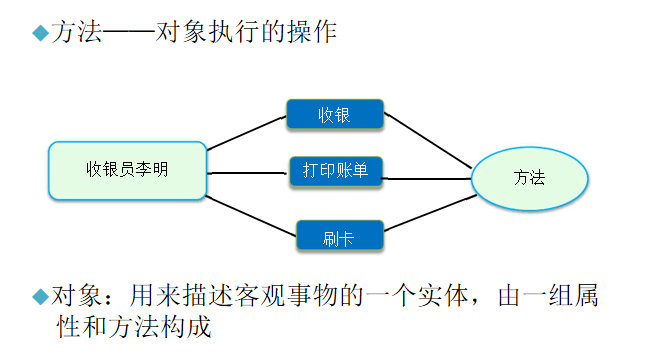
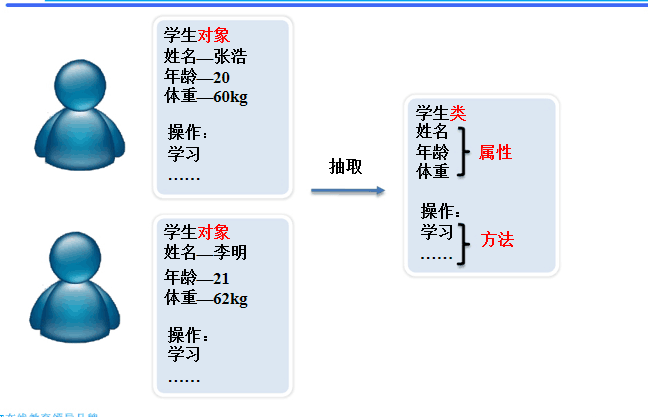
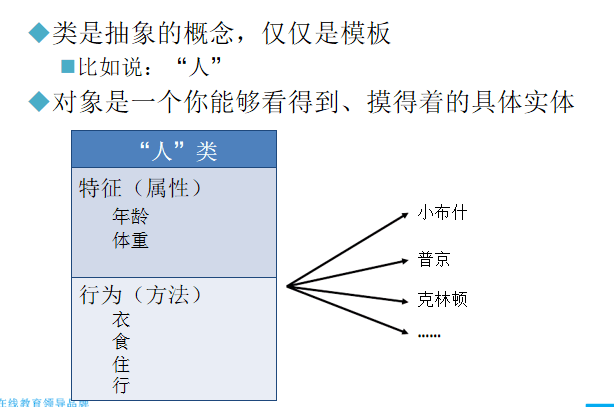
类
类:具有相同属性和方法的一组对象的集合,类是对象的抽象,对象是类的具体
类是抽象的概念,仅仅是模板
对象是一个你能够看得到,摸得着的具体实体
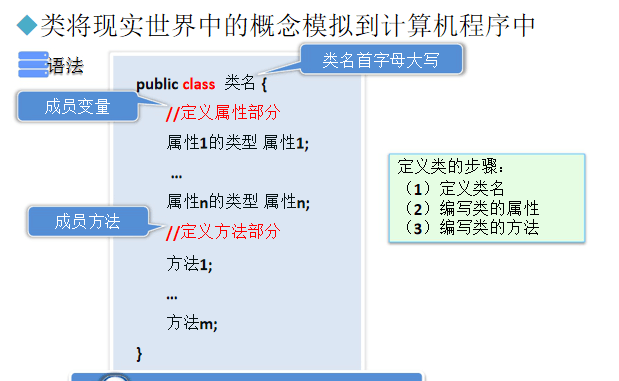
所有java程序都以类似class为组织单元
关键字class定义自定义的数据类型
访问修饰符 返回值类型,方法名(参数列表){
方法体
}
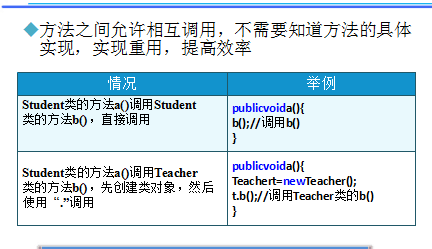
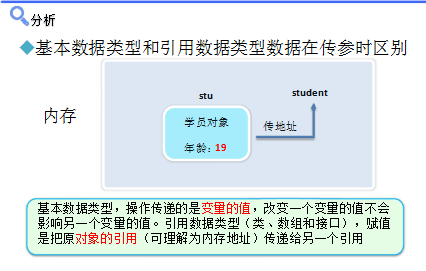
访问权限 类 包 子类 其他包 public ∨ ∨ ∨ ∨ (对任何人都是可用的) protect ∨ ∨ ∨ × (继承的类可以访问以及和private一样的权限) default ∨ ∨ × × (包访问权限,即在整个包内均可被访问) private ∨ x × × (除类型创建者和类型的内部方法之外的任何人都不能访问的元素) 当需要调用方法执行某个操作时,可以先创建类的对象,然后通过对象名.方法():来实现
1.用类打印出welcome to school
public class duixiang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
duixiang hello=new duixiang();
hello.show();
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("welcome to school");
}
}
2.用类打印出school文件的welcome to school
//school.java
package com.test;
public class school {
public void ShowShool() {
System.out.println("welcome to school");
}
}
//duixiang.java
public class duixiang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
school sc=new school();
sc.ShowShool();
}
}
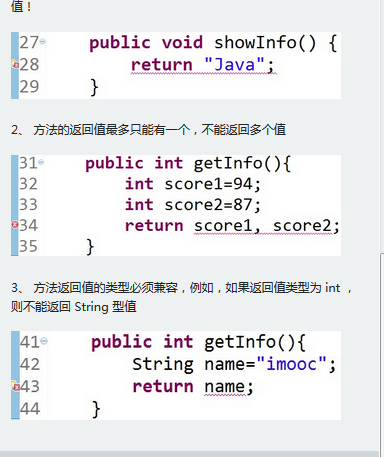
3.有返回值有参
public class school {
public static void main(String[] args) {
school hello=new school();
System.out.print(hello.show("aa"));
}
public String show(String name) {
return "欢迎您,"+name+"!";
}
}
4.无返回值有参
import java.util.Arrays;
public class helloworld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
helloworld hello=new helloworld();
int[] scores= {84,91,74,62};
hello.print(scores);
}
public void print(int[] scores) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(scores));
}
}
5.类实现两数相加
public class school {
public static void main(String[] args) {
school hello=new school();
System.out.println(hello.calc(1,2));
}
public int calc(int num1,int num2) {
int num3=num1+num2;
return num3;
}
}
6.编写学员类,输出学员信息
public class student {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student st=new student();
st.stu();
}
public static void stu() {
String name="张浩";
int age=10;
int cl=51;
String like="篮球";
System.out.println("名字是"+name);
System.out.println("年龄是"+age);
System.out.println("班级是"+cl);
System.out.println("爱好是"+like);
}
}
7.打印出[84,91,74,62]
import java.util.Arrays;
public class helloworld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
helloworld hello=new helloworld();
int[] scores= {84,91,74,62};
hello.print(scores);
}
public void print(int[] scores) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(scores));
}
}
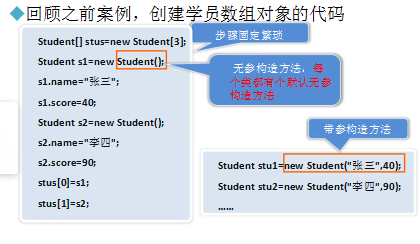
创建类名
school center=new school();
运用对象成员,使用”.”进行以下操作
引用类属性:对象名.属性
引用类的方法:对象名.方法名()
center.name=”北京中心”;给name属性赋值
center.showcenter()调用showcenter()方法

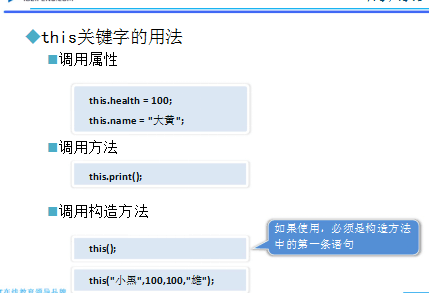
构造方法







8.输出狗和企鹅的品种和性别
//Dog.java
package com.test;
public class Dog {
/*
* 2018 12.28
* */
String name;//名字
int health;
int love;//爱心
String strain;//品种
public void eat(int num,String strain) {
System.out.println("品种为:"+strain+",吃了"+num+"狗粮");
}
public void sleep(String name,int num) {
System.out.println("名字为:"+name+",睡了"+num+"分钟");
}
}
//Penguin.java
package com.test;
public class Penguin {
String name;
String sex;
int age;
public void show(String name,String sex) {
System.out.println("企鹅名字是:"+name+",性别是"+sex);
}
}
//Demo3.java
package com.test;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog=new Dog();
dog.eat(40, "哈士奇");
Dog dog2=new Dog();
dog2.eat(20, "雪纳瑞");
Penguin p=new Penguin();
p.show("豆豆", "雄");
}
}